Understanding the Carbon to Nitrogen (C:N) Ratio and Its Importance in Cropping Systems
What is the Carbon Nitrogen Ratio?
The carbon to nitrogen ratio is a measure of comparing the mass of carbon to
nitrogen in a sample of soil. Varying ratios can have an effect on residue
decomposition, nutrient cycling, and ultimately microbial populations. Simply
put higher carbon to nitrogen ratios will decompose more slowly than lower
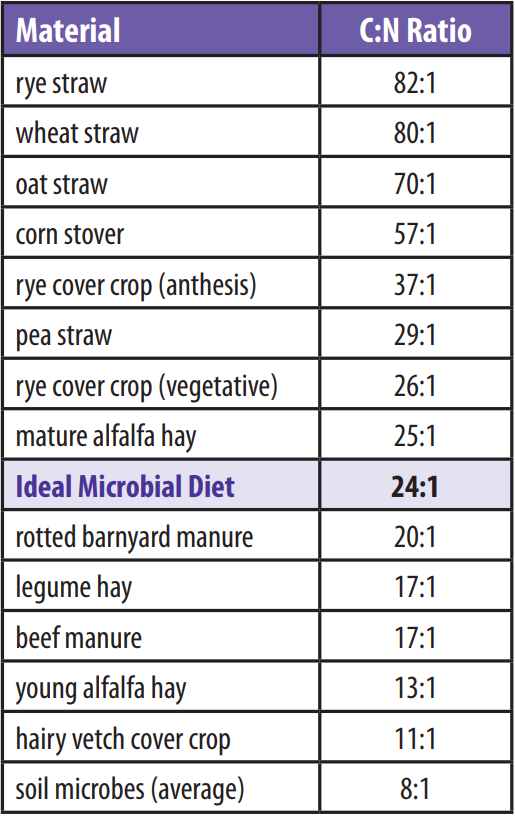
ratios. An ideal microbial diet consists of a 24:1 C:N ratio and microbes will
be most efficient at decomposing plant residues at this ratio. With a 24:1 C:N
ratio, microbes will break down residues relatively quickly so take this into
consideration when planning for soil cover.
So how should I use this knowledge to plan for cover crops?
As stated above, C:N ratios should be balanced in such a way that the microbes have a healthy diet, but ratios should be high enough to maintain soil cover. When planting cover crops, take into consideration the residue from the previous crop and the C:N ratios in the products in the cover crops. As a rule of thumb, corn does best following a low C:N ratio cover crop and soybeans do best when following a higher C:N ratio cover crop.
Recent Posts
-
The Importance of Reading Herbicide Labels for Glyphosate Tolerant Crops
Reading and interpreting a herbicide label has become increasingly difficult over the past several y …Jun 16th 2022 -
Growing High-Yielding Oats
We feel like we have always done a great job providing our growers and dealers with high quality se …Feb 24th 2022 -
Farmers Spring To Do List: Evaluate Alfalfa Winterkill
As we near the planting season, farmers are getting outside and assessing their alfalfa fiel …Jan 29th 2022


